(X)
(DC)
(CC)
(CC)
(CS6, CC)
(CC)
(CC)
(CC)
(CC)
(cmd.exe)
(File Manager)
(11)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(Full RDP session)
 ## How it works
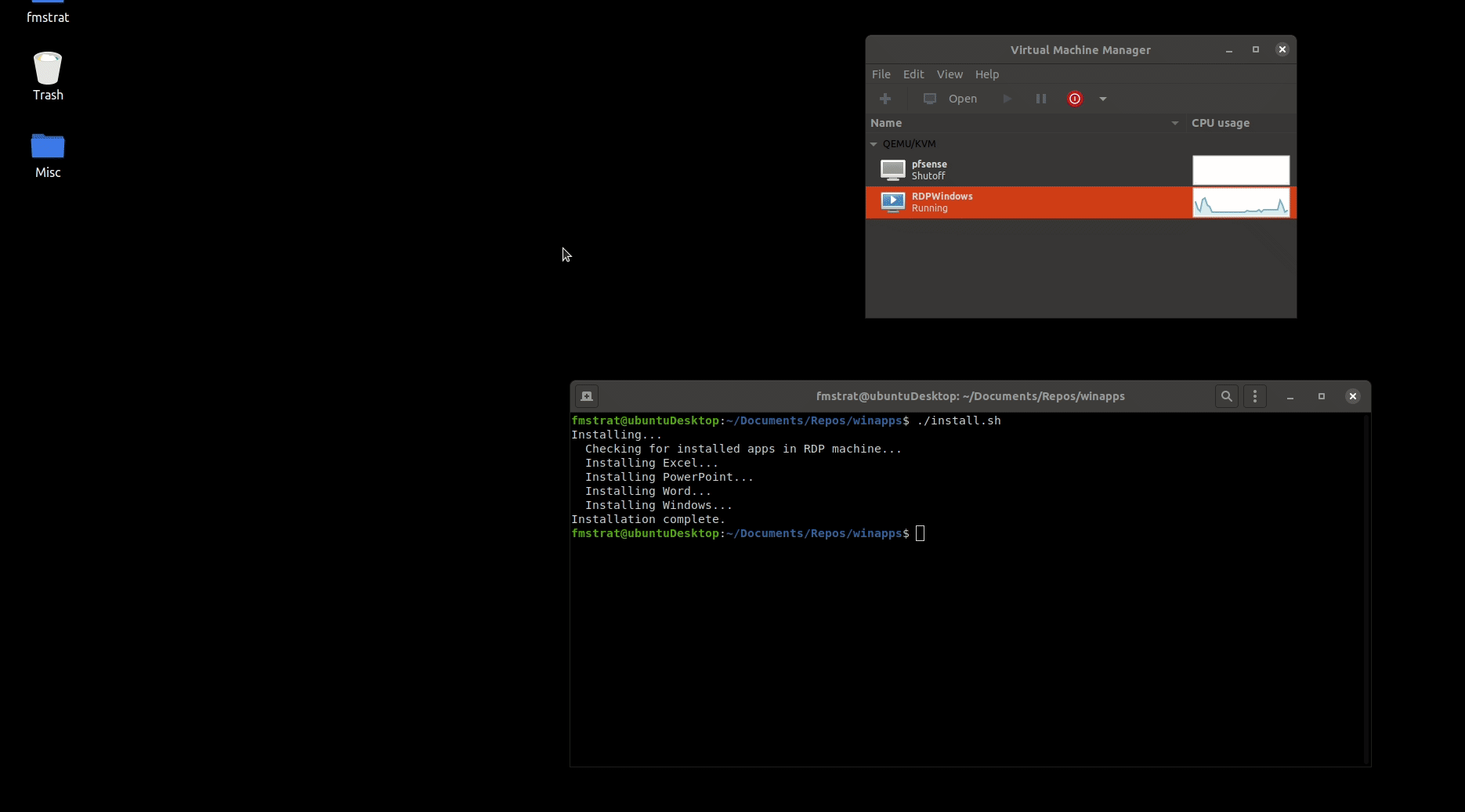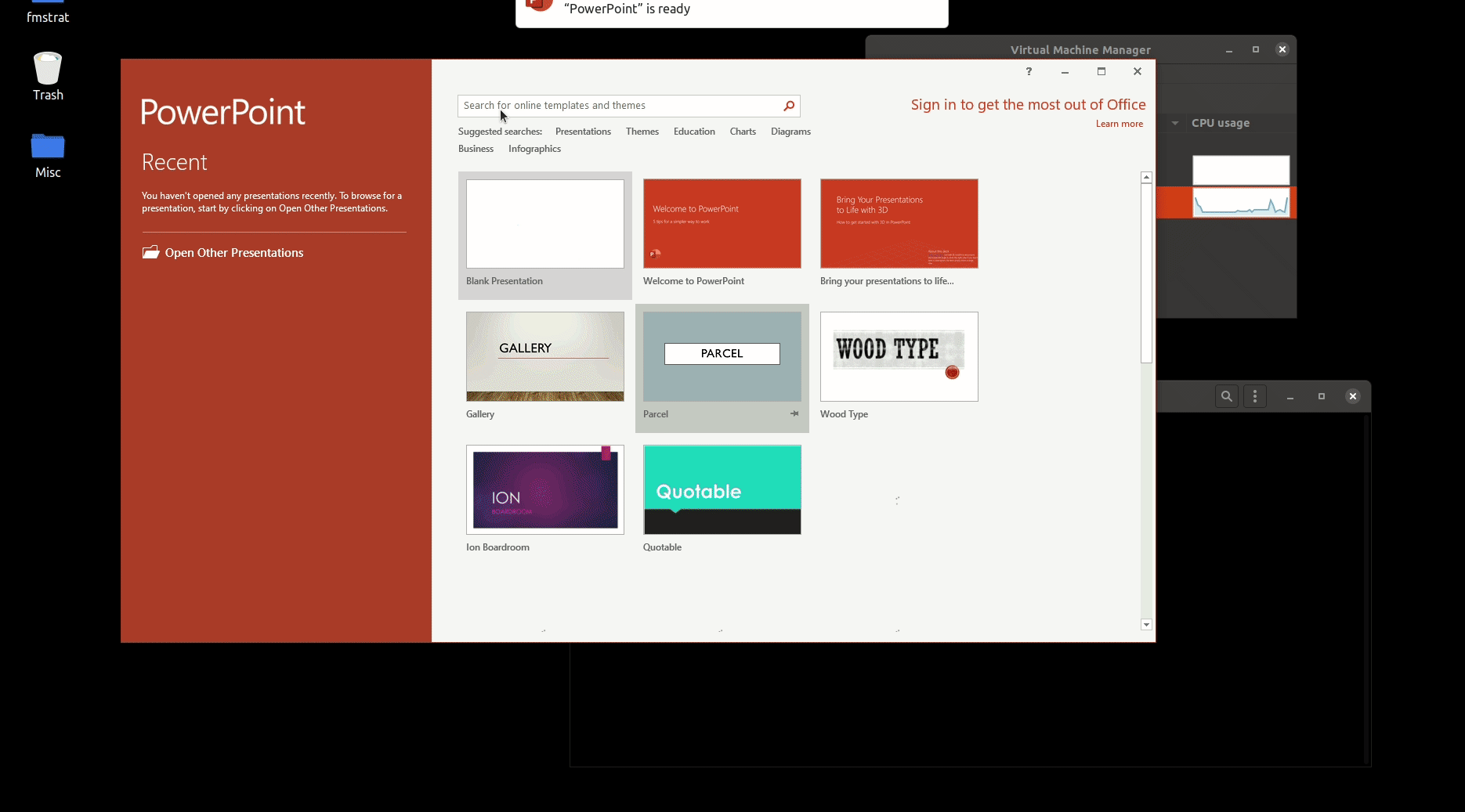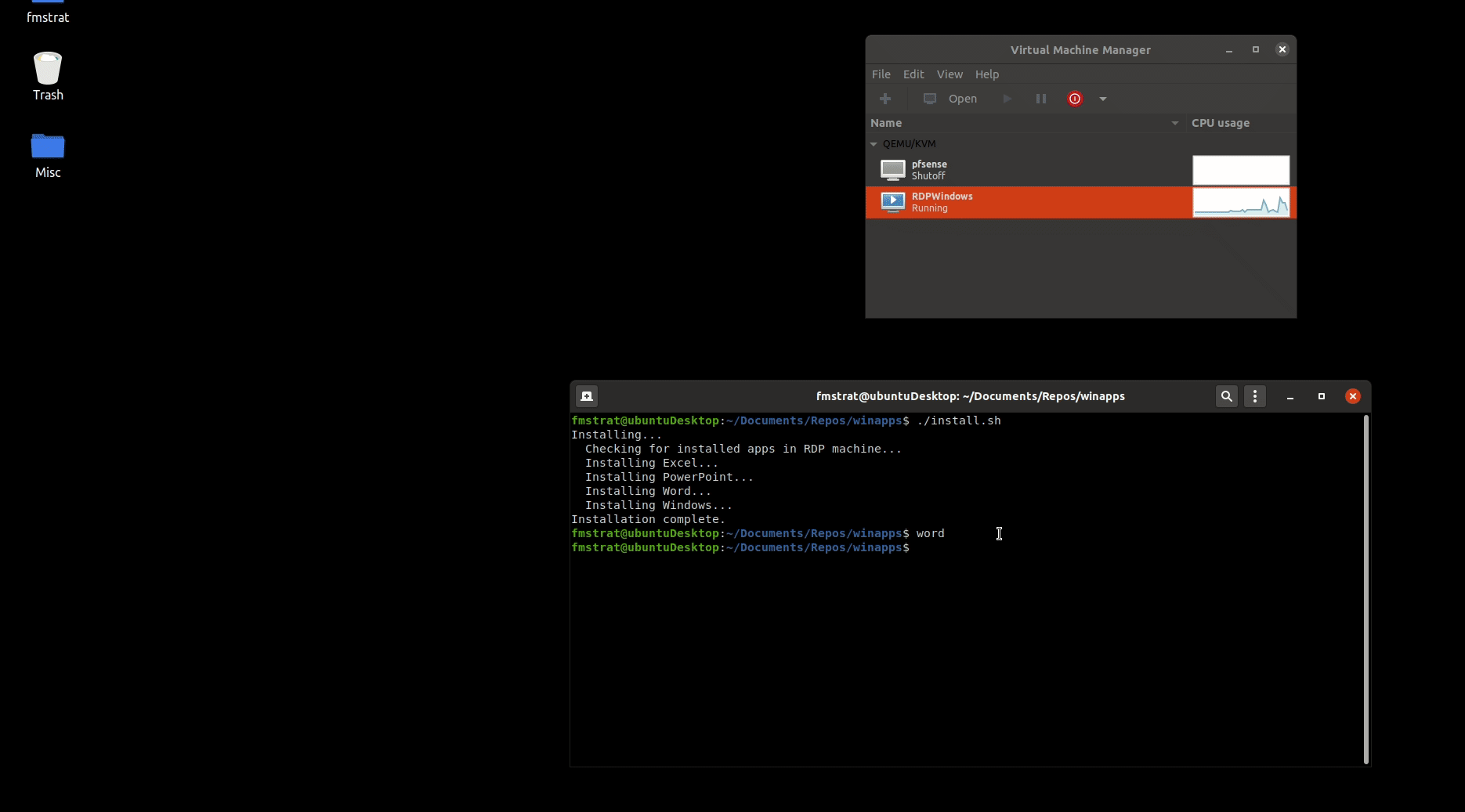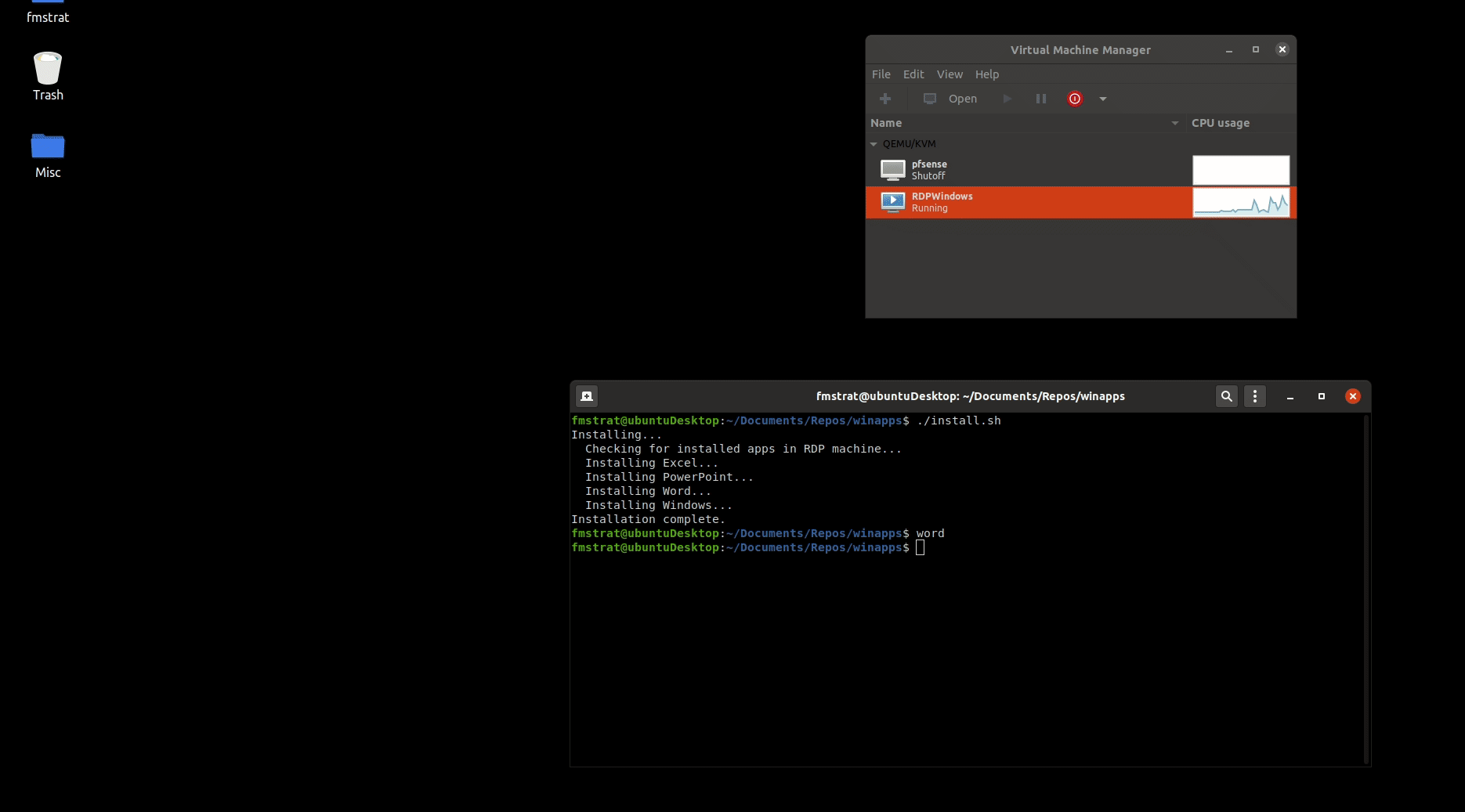
WinApps was created as an easy, one command way to include apps running inside a VM (or on any RDP server) directly into GNOME as if they were native applications. WinApps works by:
- Running a Windows RDP server in a background VM container
- Checking the RDP server for installed applications such as Microsoft Office
- If those programs are installed, it creates shortcuts leveraging FreeRDP for both the CLI and the GNOME tray
- Files in your home directory are accessible via the `\\tsclient\home` mount inside the VM
- You can right click on any files in your home directory to open with an application, too
## Currently supported applications
### WinApps supports **_ANY_** installed application on your system.
It does this by:
1. Scanning your system for offically configured applications (below)
2. Scanning your system for any other EXE files with install records in the Windows Registry
Any officially configured applications will have support for high-resolution icons and mime types for automatically detecting what files can be opened by each application. Any other detected executable files will leverage the icons pulled from the EXE.
Note: The officially configured application list below is fueled by the community, and therefore some apps may be untested by the WinApps team.
## How it works
WinApps was created as an easy, one command way to include apps running inside a VM (or on any RDP server) directly into GNOME as if they were native applications. WinApps works by:
- Running a Windows RDP server in a background VM container
- Checking the RDP server for installed applications such as Microsoft Office
- If those programs are installed, it creates shortcuts leveraging FreeRDP for both the CLI and the GNOME tray
- Files in your home directory are accessible via the `\\tsclient\home` mount inside the VM
- You can right click on any files in your home directory to open with an application, too
## Currently supported applications
### WinApps supports **_ANY_** installed application on your system.
It does this by:
1. Scanning your system for offically configured applications (below)
2. Scanning your system for any other EXE files with install records in the Windows Registry
Any officially configured applications will have support for high-resolution icons and mime types for automatically detecting what files can be opened by each application. Any other detected executable files will leverage the icons pulled from the EXE.
Note: The officially configured application list below is fueled by the community, and therefore some apps may be untested by the WinApps team.
| Adobe Acrobat Pro (X) |
Adobe Acrobat Reader (DC) |
||
| Adobe After Effects (CC) |
Adobe Audition (CC) |
||
| Adobe Bridge (CS6, CC) |
Adobe Creative Cloud (CC) |
||
| Adobe Illustrator (CC) |
Adobe InDesign (CC) |
||
| Adobe Lightroom (CC) |
Command Prompt (cmd.exe) |
||
| Explorer (File Manager) |
Internet Explorer (11) |
||
| Microsoft Access (2016, 2019, o365) |
Microsoft Excel (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| Microsoft Word (2016, 2019, o365) |
Microsoft OneNote (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| Microsoft Outlook (2016, 2019, o365) |
Microsoft PowerPoint (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| Microsoft Publisher (2016, 2019, o365) |
Powershell | ||
| Windows (Full RDP session) |
 ## Adding pre-defined applications
Adding applications with custom icons and mime types to the installer is easy. Simply copy one of the application configurations in the `apps` folder, and:
- Edit the variables for the application
- Replace the `icon.svg` with an SVG for the application (appropriately licensed)
- Re-run the installer
- Submit a Pull Request to add it to WinApps officially
When running the installer, it will check for if any configured apps are installed, and if they are it will create the appropriate shortcuts on the host OS.
## Running applications manually
WinApps offers a manual mode for running applications that are not configured. This is completed with the `manual` flag. Executables that are in the path do not require full path definition.
```bash
./bin/winapps manual "C:\my\directory\executableNotInPath.exe"
./bin/winapps manual executableInPath.exe
```
## Checking for new application support
The installer can be run multiple times, so simply run the below again and it will remove any current installations and update for the latest applications.
```bash
./installer.sh
```
## Optional installer command line arguments
The following optional commands can be used to manage your application configurations without prompts:
```bash
./installer.sh --user # Configure applications for the current user
./installer.sh --system # Configure applications for the entire system
./installer.sh --user --uninstall # Remove all configured applications for the current user
./installer.sh --system --uninstall # Remove all configured applications for the entire system
./installer.sh --user --setupAllOfficiallySupportedApps # Configures all officially supported applications for the current user
./installer.sh --system --setupAllOfficiallySupportedApps # Configures all officially supported applications for the entire system
```
## Shout outs
- Some icons pulled from
- Fluent UI React - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluent-ui-react/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- Fluent UI - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluentui/blob/master/LICENSE) with [restricted use](https://static2.sharepointonline.com/files/fabric/assets/microsoft_fabric_assets_license_agreement_nov_2019.pdf)
- PKief's VSCode Material Icon Theme - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/vscode-material-icon-theme/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- DiemenDesign's LibreICONS - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/LibreICONS/blob/master/LICENSE)
## Adding pre-defined applications
Adding applications with custom icons and mime types to the installer is easy. Simply copy one of the application configurations in the `apps` folder, and:
- Edit the variables for the application
- Replace the `icon.svg` with an SVG for the application (appropriately licensed)
- Re-run the installer
- Submit a Pull Request to add it to WinApps officially
When running the installer, it will check for if any configured apps are installed, and if they are it will create the appropriate shortcuts on the host OS.
## Running applications manually
WinApps offers a manual mode for running applications that are not configured. This is completed with the `manual` flag. Executables that are in the path do not require full path definition.
```bash
./bin/winapps manual "C:\my\directory\executableNotInPath.exe"
./bin/winapps manual executableInPath.exe
```
## Checking for new application support
The installer can be run multiple times, so simply run the below again and it will remove any current installations and update for the latest applications.
```bash
./installer.sh
```
## Optional installer command line arguments
The following optional commands can be used to manage your application configurations without prompts:
```bash
./installer.sh --user # Configure applications for the current user
./installer.sh --system # Configure applications for the entire system
./installer.sh --user --uninstall # Remove all configured applications for the current user
./installer.sh --system --uninstall # Remove all configured applications for the entire system
./installer.sh --user --setupAllOfficiallySupportedApps # Configures all officially supported applications for the current user
./installer.sh --system --setupAllOfficiallySupportedApps # Configures all officially supported applications for the entire system
```
## Shout outs
- Some icons pulled from
- Fluent UI React - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluent-ui-react/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- Fluent UI - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluentui/blob/master/LICENSE) with [restricted use](https://static2.sharepointonline.com/files/fabric/assets/microsoft_fabric_assets_license_agreement_nov_2019.pdf)
- PKief's VSCode Material Icon Theme - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/vscode-material-icon-theme/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- DiemenDesign's LibreICONS - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/LibreICONS/blob/master/LICENSE)