(X)
(CC)
(CC)
(CS6, CC)
(CC)
(CC)
(CC)
(CC)
(cmd.exe)
(File Manager)
(11)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(2016, 2019, o365)
(Full RDP session)
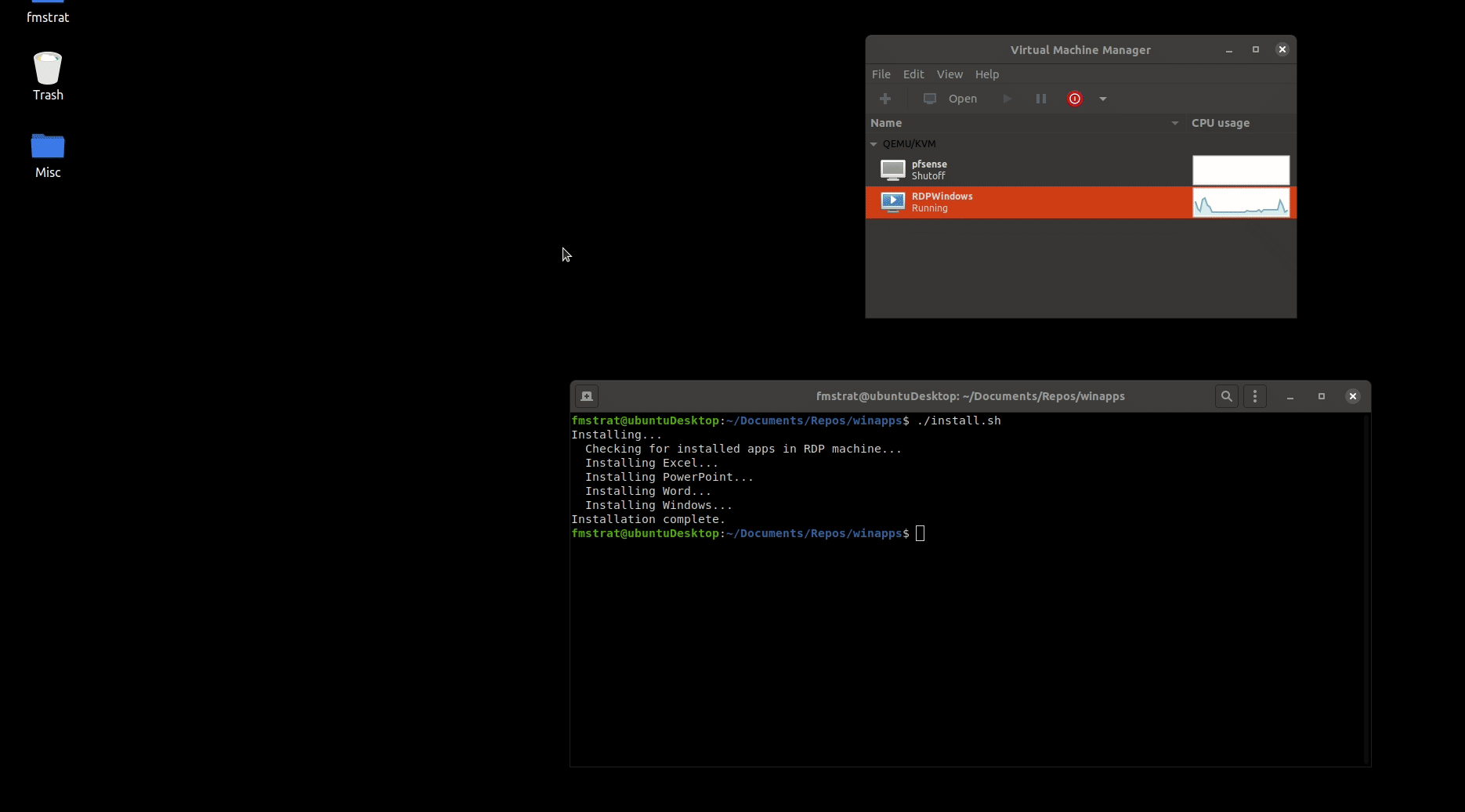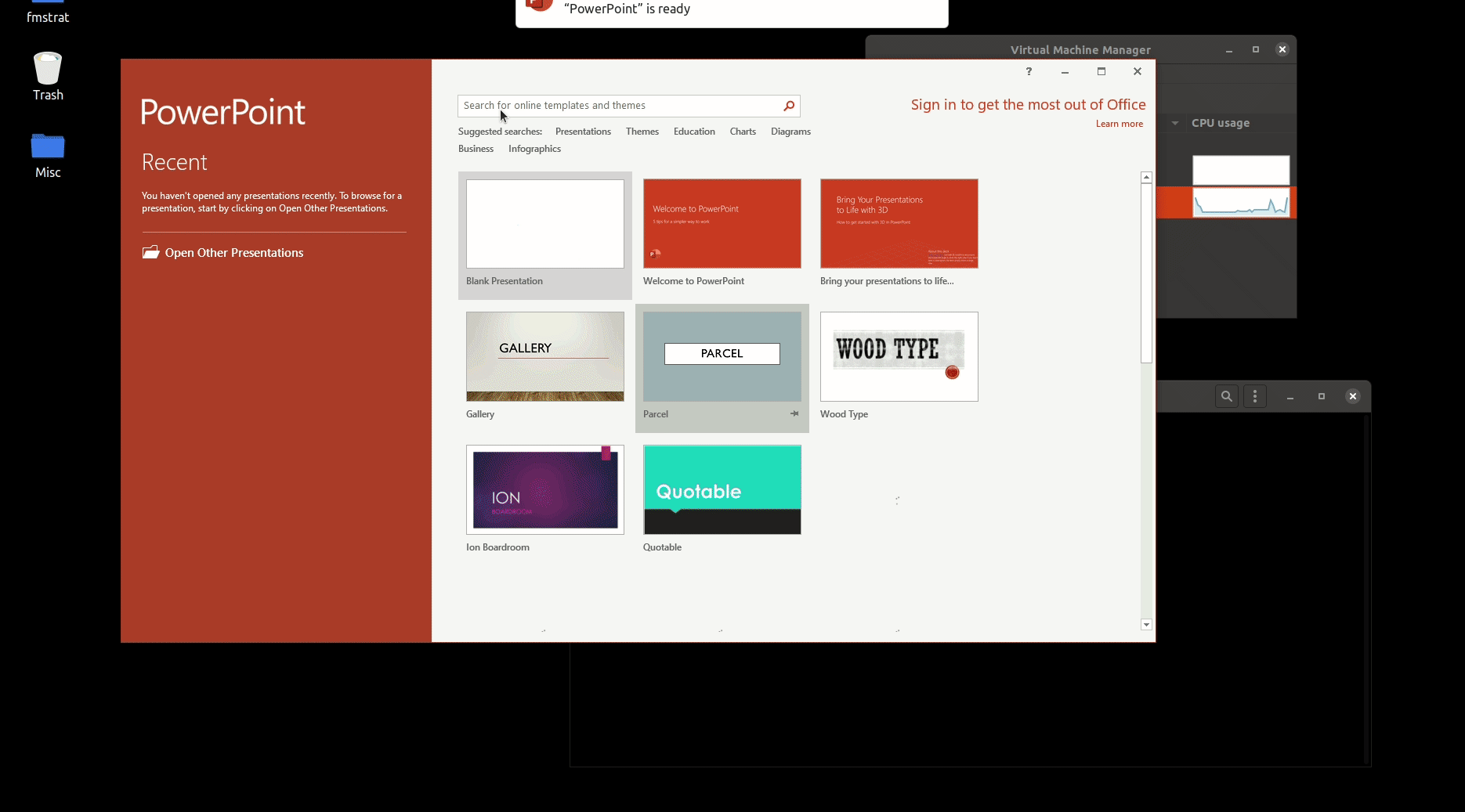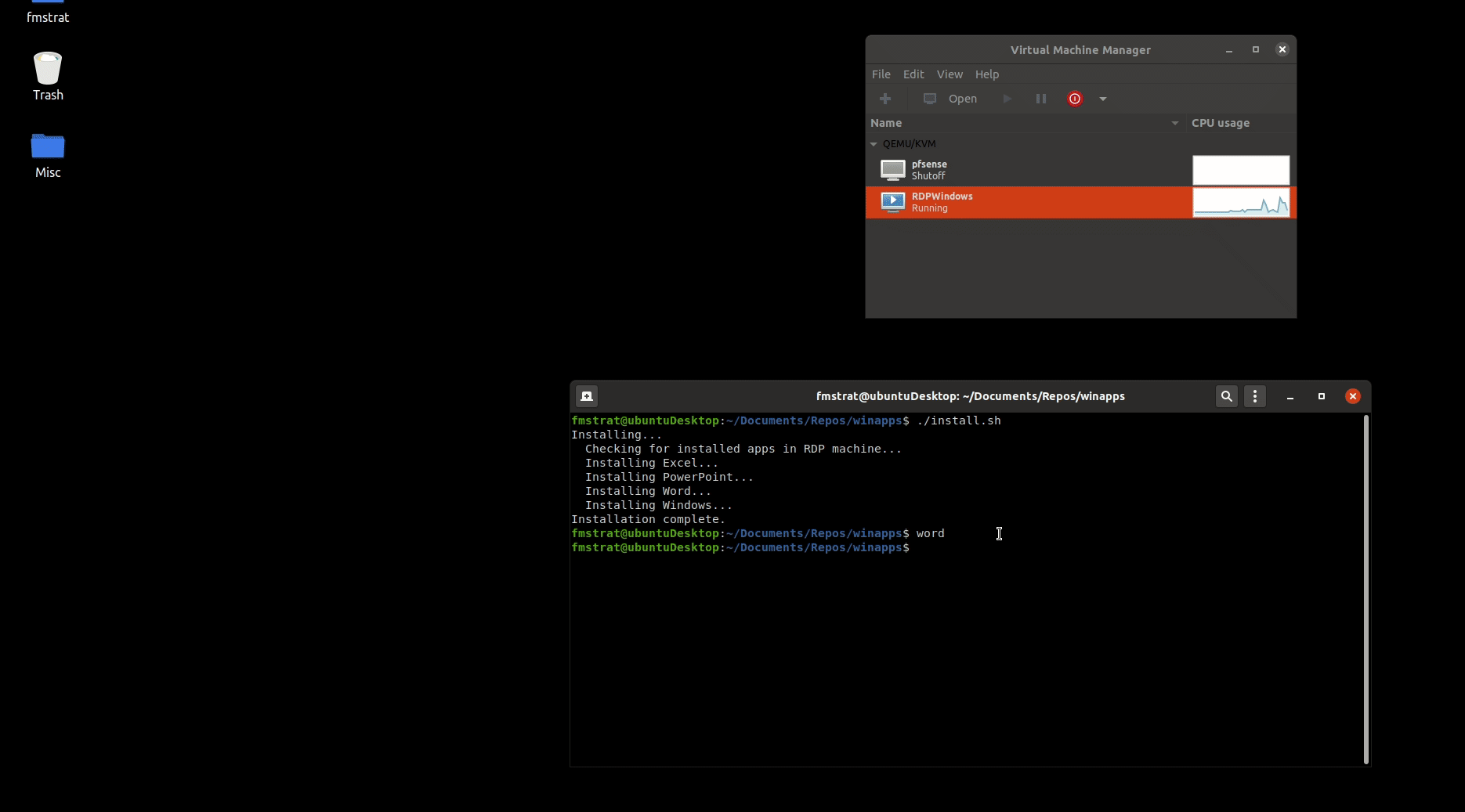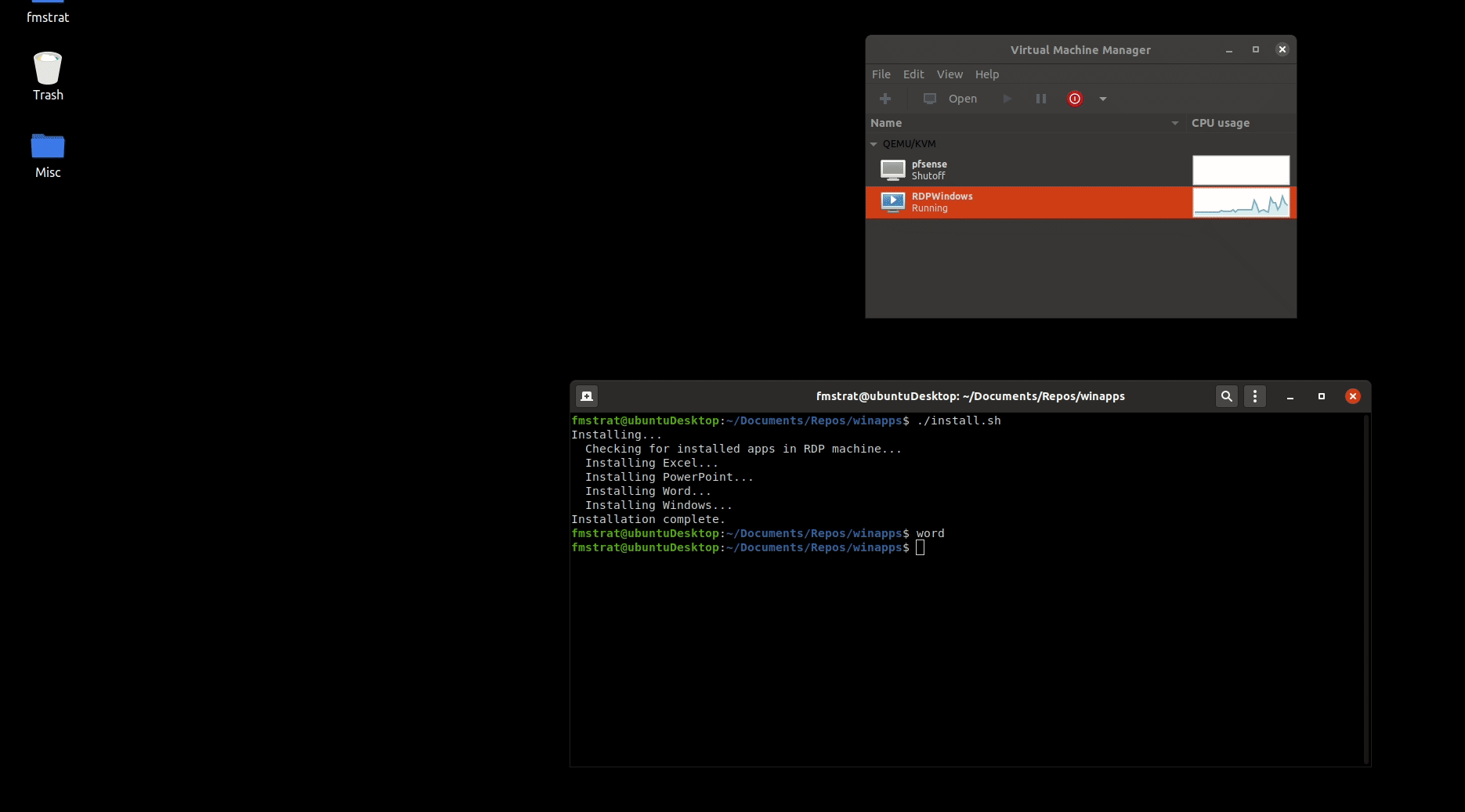 ## Underlying Mechanism
WinApps works by:
1. Running Windows in a `Docker` or `libvirt + KVM/QEMU` virtual machine (deprecated).
2. Querying Windows for all installed applications.
3. Creating shortcuts to selected Windows applications on the host GNU/Linux OS.
4. Using [`FreeRDP`](https://www.freerdp.com/) as a backend to seamlessly render Windows applications alongside GNU/Linux applications.
## Additional Features
- The GNU/Linux `/home` directory is accessible within Windows via the `\\tsclient\home` mount.
- Integration with `Nautilus`, allowing you to right-click files to open them with specific Windows applications based on the file MIME type.
## Supported Applications
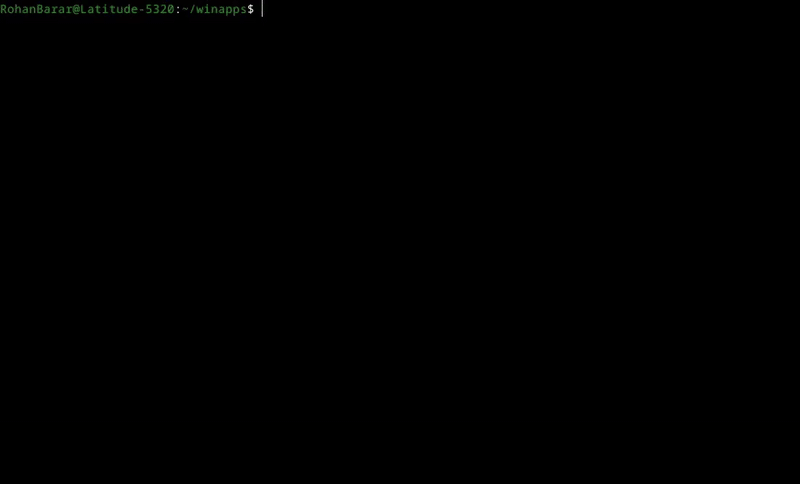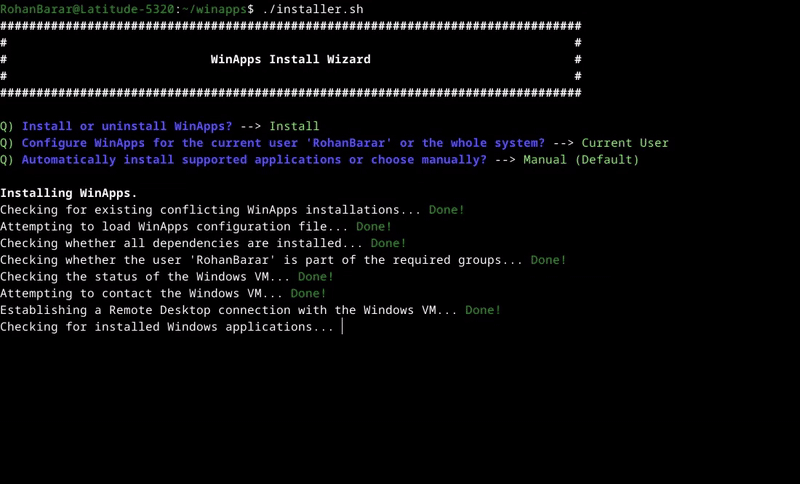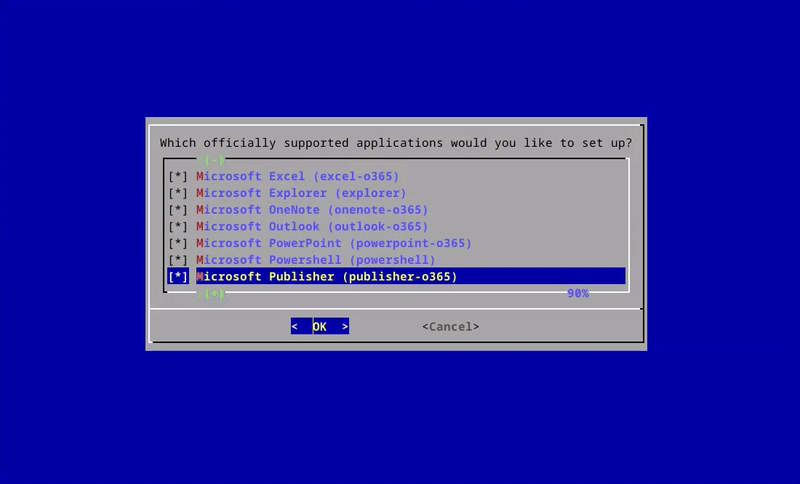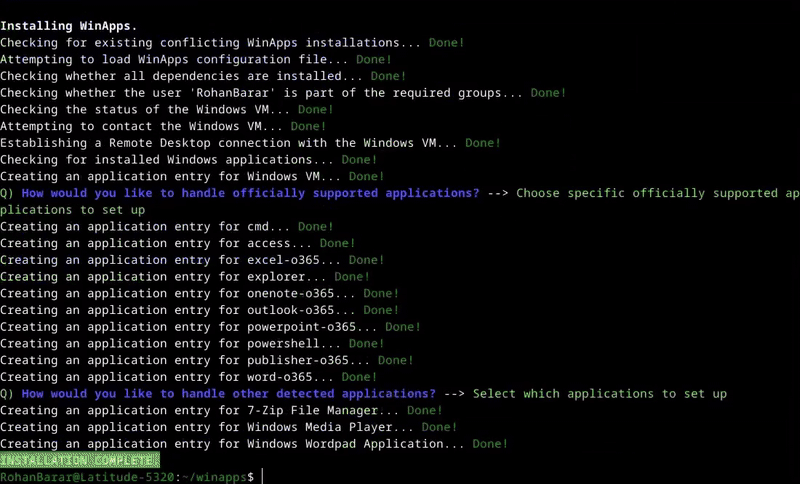
**WinApps supports *ALL* Windows applications.**
Universal application support is achieved by:
1. Scanning Windows for any officially supported applications (list below).
2. Scanning Windows for any other `.exe` files listed within the Windows Registry.
Officially supported applications benefit from high-resolution icons and pre-populated MIME types. This enables file managers to determine which Windows applications should open files based on file extensions. Icons for other detected applications are pulled from `.exe` files.
Contributing to the list of supported applications is encouraged through submission of pull requests! Please help us grow the WinApps community.
*Please note that the provided list of officially supported applications is community-driven. As such, some applications may not be tested and verified by the WinApps team.*
### Officially Supported Applications
## Underlying Mechanism
WinApps works by:
1. Running Windows in a `Docker` or `libvirt + KVM/QEMU` virtual machine (deprecated).
2. Querying Windows for all installed applications.
3. Creating shortcuts to selected Windows applications on the host GNU/Linux OS.
4. Using [`FreeRDP`](https://www.freerdp.com/) as a backend to seamlessly render Windows applications alongside GNU/Linux applications.
## Additional Features
- The GNU/Linux `/home` directory is accessible within Windows via the `\\tsclient\home` mount.
- Integration with `Nautilus`, allowing you to right-click files to open them with specific Windows applications based on the file MIME type.
## Supported Applications
**WinApps supports *ALL* Windows applications.**
Universal application support is achieved by:
1. Scanning Windows for any officially supported applications (list below).
2. Scanning Windows for any other `.exe` files listed within the Windows Registry.
Officially supported applications benefit from high-resolution icons and pre-populated MIME types. This enables file managers to determine which Windows applications should open files based on file extensions. Icons for other detected applications are pulled from `.exe` files.
Contributing to the list of supported applications is encouraged through submission of pull requests! Please help us grow the WinApps community.
*Please note that the provided list of officially supported applications is community-driven. As such, some applications may not be tested and verified by the WinApps team.*
### Officially Supported Applications
| Adobe Acrobat Pro (X) |
Adobe After Effects (CC) |
||
| Adobe Audition (CC) |
Adobe Bridge (CS6, CC) |
||
| Adobe Creative Cloud (CC) |
Adobe Illustrator (CC) |
||
| Adobe InDesign (CC) |
Adobe Lightroom (CC) |
||
| Command Prompt (cmd.exe) |
Explorer (File Manager) |
||
| Internet Explorer (11) |
Microsoft Access (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| Microsoft Excel (2016, 2019, o365) |
Microsoft Word (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| Microsoft OneNote (2016, 2019, o365) |
Microsoft Outlook (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| Microsoft PowerPoint (2016, 2019, o365) |
Microsoft Publisher (2016, 2019, o365) |
||
| PowerShell | Windows (Full RDP session) |
 ## Adding Additional Pre-defined Applications
Adding your own applications with custom icons and MIME types to the installer is easy. Simply copy one of the application configurations in the `apps` folder located within the WinApps repository, and:
1. Modify the name and variables to reflect the appropriate/desired values for your application.
2. Replace `icon.svg` with an SVG for your application (ensuring the icon is appropriately licensed).
3. Remove and reinstall WinApps.
4. (Optional, but strongly encouraged) Submit a pull request to add your application to WinApps as an officially supported application once you have tested your configuration files to verify functionality.
## Running Applications Manually
WinApps offers a manual mode for running applications that were not configured by the WinApps installer. This is completed with the `manual` flag. Executables that are in the Windows PATH do not require full path definition.
```bash
./bin/winapps manual "C:\my\directory\executableNotInPath.exe"
./bin/winapps manual executableInPath.exe
```
## Updating WinApps
The installer can be run multiple times. To update your installation of WinApps:
1. Run the WinApps installer to remove WinApps from your system.
2. Pull the latest changes from the WinApps GitHub repository.
3. Re-install WinApps using the WinApps installer.
## Shout-outs
Some icons used for the officially supported applications were sourced from:
- Fluent UI React - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluent-ui-react/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- Fluent UI - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluentui/blob/master/LICENSE) with [restricted use](https://static2.sharepointonline.com/files/fabric/assets/microsoft_fabric_assets_license_agreement_nov_2019.pdf)
- PKief's VSCode Material Icon Theme - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/vscode-material-icon-theme/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- DiemenDesign's LibreICONS - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/LibreICONS/blob/master/LICENSE)
## Adding Additional Pre-defined Applications
Adding your own applications with custom icons and MIME types to the installer is easy. Simply copy one of the application configurations in the `apps` folder located within the WinApps repository, and:
1. Modify the name and variables to reflect the appropriate/desired values for your application.
2. Replace `icon.svg` with an SVG for your application (ensuring the icon is appropriately licensed).
3. Remove and reinstall WinApps.
4. (Optional, but strongly encouraged) Submit a pull request to add your application to WinApps as an officially supported application once you have tested your configuration files to verify functionality.
## Running Applications Manually
WinApps offers a manual mode for running applications that were not configured by the WinApps installer. This is completed with the `manual` flag. Executables that are in the Windows PATH do not require full path definition.
```bash
./bin/winapps manual "C:\my\directory\executableNotInPath.exe"
./bin/winapps manual executableInPath.exe
```
## Updating WinApps
The installer can be run multiple times. To update your installation of WinApps:
1. Run the WinApps installer to remove WinApps from your system.
2. Pull the latest changes from the WinApps GitHub repository.
3. Re-install WinApps using the WinApps installer.
## Shout-outs
Some icons used for the officially supported applications were sourced from:
- Fluent UI React - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluent-ui-react/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- Fluent UI - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/fluentui/blob/master/LICENSE) with [restricted use](https://static2.sharepointonline.com/files/fabric/assets/microsoft_fabric_assets_license_agreement_nov_2019.pdf)
- PKief's VSCode Material Icon Theme - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/vscode-material-icon-theme/blob/master/LICENSE.md)
- DiemenDesign's LibreICONS - Icons under [MIT License](https://github.com/Fmstrat/LibreICONS/blob/master/LICENSE)